The Power of GIS for Homeland Security

- Vinaybabu Pasam
- December 26, 2024
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) have become an indispensable tool in homeland security, providing agencies and organizations with the critical insights necessary for informed decision-making and rapid response. GIS technology enables the mapping, analysis, and visualization of spatial data, which is crucial for managing a wide range of security challenges—from disaster response to counterterrorism efforts.
In this blog, we’ll explore how GIS plays a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of homeland security operations, ensuring public safety, and responding to emergencies with greater precision and speed.
GIS and Threat Detection
Homeland security often involves tracking and mitigating potential threats—whether from natural disasters, terrorism, or other emergencies. GIS serves as a powerful tool to support threat detection and prediction. By integrating real-time data from a variety of sources—such as surveillance cameras, sensor networks, and social media—GIS platforms enable analysts to monitor and assess potential threats quickly and effectively.

For example, GIS can be used to monitor suspicious activities at key infrastructure sites or high-profile events. By mapping out areas of interest and overlaying them with real-time data, security personnel can pinpoint abnormal patterns or unusual concentrations of activity, allowing for early intervention before a threat escalates.
Emergency Response and Disaster Management
In emergency management, GIS provides a comprehensive approach to disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. Whether it’s a natural disaster like a hurricane or a man-made crisis such as a terrorist attack, GIS allows emergency responders to quickly assess the situation, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate resources effectively.

For instance, during an evacuation, GIS can be used to identify the safest and fastest routes for civilians, taking into account factors such as road conditions, traffic patterns, and environmental hazards. By leveraging GIS, agencies can improve situational awareness, prioritize efforts, and ensure a more efficient response, ultimately saving lives.
Critical Infrastructure Protection
Securing critical infrastructure, such as power plants, transportation networks, and communication systems, is a major focus of homeland security efforts. GIS plays an essential role in mapping and analyzing the vulnerabilities of these infrastructures, as well as in planning and coordinating their protection.

With GIS, homeland security agencies can perform detailed risk assessments to identify areas that are most susceptible to threats, including natural disasters or terrorist attacks. By modeling various risk scenarios, agencies can better allocate resources, fortify key infrastructure, and develop effective protection strategies to reduce the impact of potential attacks.
Surveillance and Border Security
Maintaining border security is a complex challenge that demands the integration of multiple technologies and data sources. GIS enables law enforcement and border control agencies to analyze geospatial data from satellite imagery, drones, and ground sensors to monitor borders, identify illegal crossings, and track the movement of individuals or vehicles.
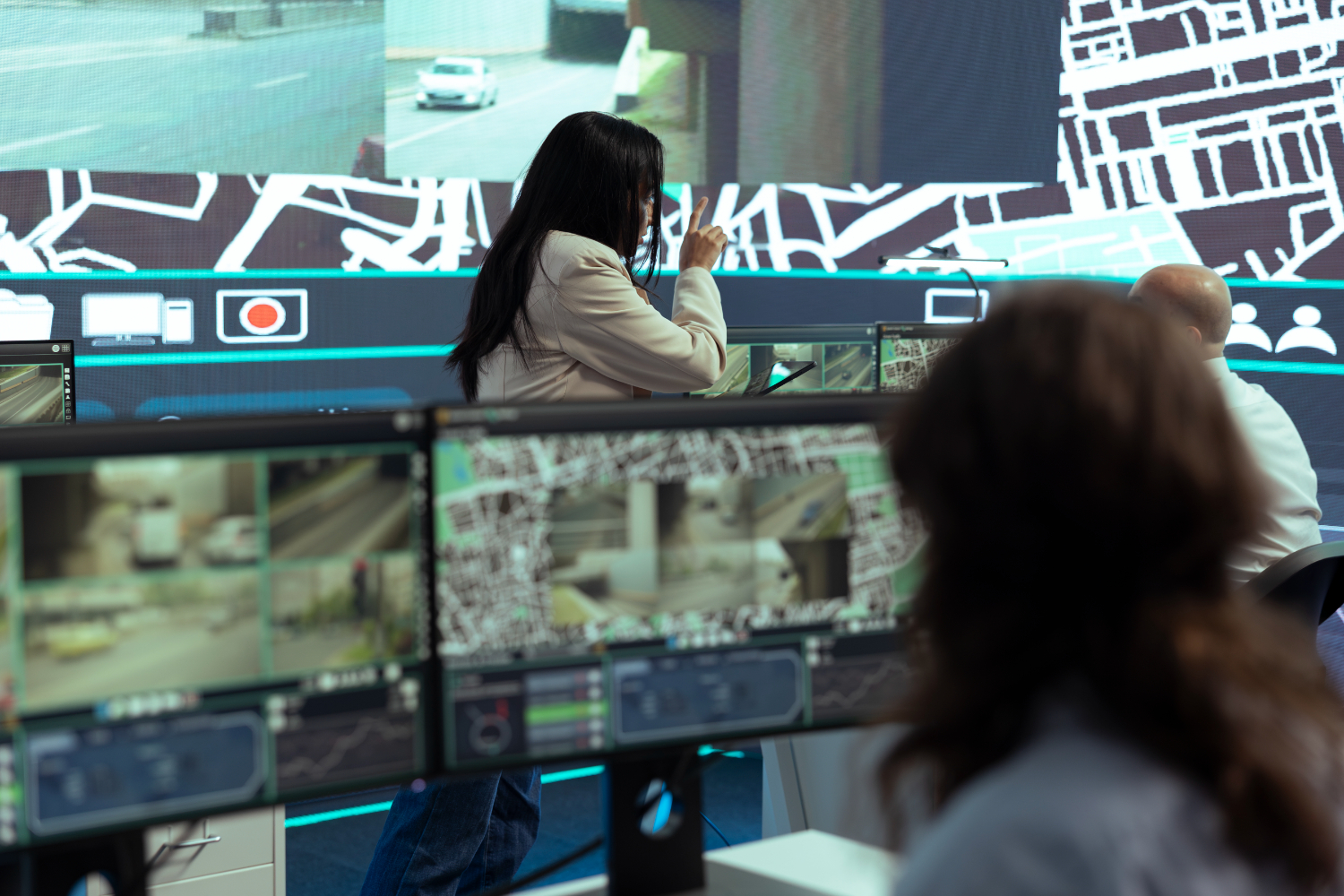

In addition, GIS can be integrated with other security systems, such as facial recognition or vehicle license plate tracking, to provide a more comprehensive picture of activity along borders. By visualizing movement patterns in real-time, authorities can make quicker decisions, deploy resources to critical areas, and even predict potential breaches before they occur.
Data Integration and Decision Support
One of the most valuable features of GIS in homeland security is its ability to integrate data from a wide range of sources into a single platform. From social media feeds to satellite imagery, GIS helps create a unified view of a security situation. This is critical for decision-makers who rely on up-to-date, accurate data to manage complex security operations.
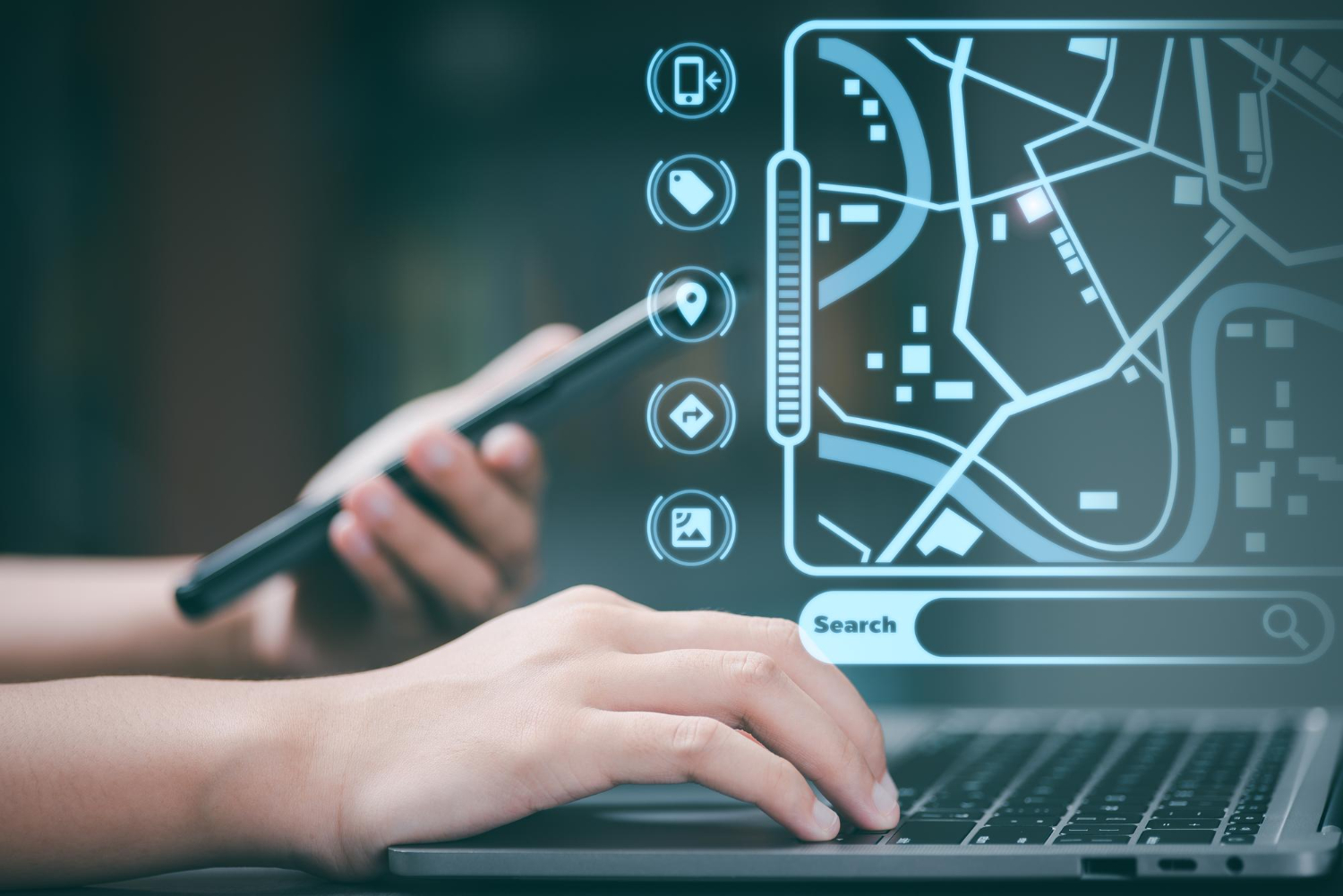

GIS platforms like ArcGIS Pro allow users to combine disparate data layers—such as infrastructure maps, demographic data, and environmental conditions—into a cohesive, actionable map. This enhances decision support, as officials can visualize and analyze multiple factors simultaneously, making it easier to assess risks, allocate resources, and plan interventions.
Training and Simulation
Another key aspect of GIS in homeland security is its role in training and simulation. GIS-based simulation tools allow security agencies to create realistic training scenarios for their personnel. Whether it’s preparing for a terrorist attack, a cyber threat, or a natural disaster, GIS can simulate various emergency situations and help personnel practice their responses.

For example, a simulated terrorist attack in a crowded urban area can be modeled with GIS, allowing responders to plan evacuation routes, coordinate resources, and assess the effectiveness of different strategies. These simulations provide invaluable practice and preparation for real-world events, improving response times and outcomes when disaster strikes.
The Future of GIS in Homeland Security
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the potential of GIS in homeland security. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics are opening up new possibilities for security applications. GIS platforms are becoming more sophisticated, capable of handling vast amounts of data from diverse sources and providing real-time insights to decision-makers.

One of the most exciting developments is the integration of GIS with unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and drones. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture critical data in hard-to-reach areas, such as disaster zones or remote borders. This data can be fed into GIS systems for real-time analysis, offering a dynamic view of the situation on the ground.
Geospatial technologies are transforming the landscape of homeland security, providing agencies with the tools they need to respond quickly and effectively to emerging threats. From enhancing situational awareness to improving response times, GIS is at the heart of modern security strategies.
As GIS technology continues to evolve, its role in homeland security will only become more integral. Whether it’s through better threat detection, faster disaster response, or more effective infrastructure protection, GIS is helping to ensure a safer, more secure world for all.
By leveraging the full potential of GIS, homeland security agencies can stay one step ahead, making smarter, data-driven decisions that protect people, infrastructure, and national security.

- Vinaybabu Pasam
- December 26, 2024
The Power of GIS for Homeland Security
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) have become an indispensable tool in homeland security, providing agencies and organizations with the critical insights necessary for informed decision-making and rapid response. GIS technology enables the mapping, analysis, and visualization of spatial data, which is crucial for managing a wide range of security challenges—from disaster response to counterterrorism efforts.
In this blog, we’ll explore how GIS plays a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of homeland security operations, ensuring public safety, and responding to emergencies with greater precision and speed.
GIS and Threat Detection
Homeland security often involves tracking and mitigating potential threats—whether from natural disasters, terrorism, or other emergencies. GIS serves as a powerful tool to support threat detection and prediction. By integrating real-time data from a variety of sources—such as surveillance cameras, sensor networks, and social media—GIS platforms enable analysts to monitor and assess potential threats quickly and effectively.

For example, GIS can be used to monitor suspicious activities at key infrastructure sites or high-profile events. By mapping out areas of interest and overlaying them with real-time data, security personnel can pinpoint abnormal patterns or unusual concentrations of activity, allowing for early intervention before a threat escalates.
Emergency Response and Disaster Management
In emergency management, GIS provides a comprehensive approach to disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. Whether it’s a natural disaster like a hurricane or a man-made crisis such as a terrorist attack, GIS allows emergency responders to quickly assess the situation, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate resources effectively.

For instance, during an evacuation, GIS can be used to identify the safest and fastest routes for civilians, taking into account factors such as road conditions, traffic patterns, and environmental hazards. By leveraging GIS, agencies can improve situational awareness, prioritize efforts, and ensure a more efficient response, ultimately saving lives.
Critical Infrastructure Protection
Securing critical infrastructure, such as power plants, transportation networks, and communication systems, is a major focus of homeland security efforts. GIS plays an essential role in mapping and analyzing the vulnerabilities of these infrastructures, as well as in planning and coordinating their protection.

With GIS, homeland security agencies can perform detailed risk assessments to identify areas that are most susceptible to threats, including natural disasters or terrorist attacks. By modeling various risk scenarios, agencies can better allocate resources, fortify key infrastructure, and develop effective protection strategies to reduce the impact of potential attacks.
Surveillance and Border Security
Maintaining border security is a complex challenge that demands the integration of multiple technologies and data sources. GIS enables law enforcement and border control agencies to analyze geospatial data from satellite imagery, drones, and ground sensors to monitor borders, identify illegal crossings, and track the movement of individuals or vehicles.

In addition, GIS can be integrated with other security systems, such as facial recognition or vehicle license plate tracking, to provide a more comprehensive picture of activity along borders. By visualizing movement patterns in real-time, authorities can make quicker decisions, deploy resources to critical areas, and even predict potential breaches before they occur.
Data Integration and Decision Support
One of the most valuable features of GIS in homeland security is its ability to integrate data from a wide range of sources into a single platform. From social media feeds to satellite imagery, GIS helps create a unified view of a security situation. This is critical for decision-makers who rely on up-to-date, accurate data to manage complex security operations.

GIS platforms like ArcGIS Pro allow users to combine disparate data layers—such as infrastructure maps, demographic data, and environmental conditions—into a cohesive, actionable map. This enhances decision support, as officials can visualize and analyze multiple factors simultaneously, making it easier to assess risks, allocate resources, and plan interventions.
Training and Simulation
Another key aspect of GIS in homeland security is its role in training and simulation. GIS-based simulation tools allow security agencies to create realistic training scenarios for their personnel. Whether it’s preparing for a terrorist attack, a cyber threat, or a natural disaster, GIS can simulate various emergency situations and help personnel practice their responses.

For example, a simulated terrorist attack in a crowded urban area can be modeled with GIS, allowing responders to plan evacuation routes, coordinate resources, and assess the effectiveness of different strategies. These simulations provide invaluable practice and preparation for real-world events, improving response times and outcomes when disaster strikes.
The Future of GIS in Homeland Security
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the potential of GIS in homeland security. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics are opening up new possibilities for security applications. GIS platforms are becoming more sophisticated, capable of handling vast amounts of data from diverse sources and providing real-time insights to decision-makers.

One of the most exciting developments is the integration of GIS with unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and drones. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture critical data in hard-to-reach areas, such as disaster zones or remote borders. This data can be fed into GIS systems for real-time analysis, offering a dynamic view of the situation on the ground.
Geospatial technologies are transforming the landscape of homeland security, providing agencies with the tools they need to respond quickly and effectively to emerging threats. From enhancing situational awareness to improving response times, GIS is at the heart of modern security strategies.
As GIS technology continues to evolve, its role in homeland security will only become more integral. Whether it’s through better threat detection, faster disaster response, or more effective infrastructure protection, GIS is helping to ensure a safer, more secure world for all.
By leveraging the full potential of GIS, homeland security agencies can stay one step ahead, making smarter, data-driven decisions that protect people, infrastructure, and national security.