How GIS Technology is Revolutionizing the Mining Industry

- Vinaybabu Pasam
- December 26, 2024
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) have rapidly evolved from a niche technology to a cornerstone of industries across the world, and the mining sector is no exception. GIS offers transformative solutions for nearly every phase of mining, from exploration to extraction, logistics, environmental management, and beyond. By combining spatial data with advanced analysis tools, GIS helps mining companies increase efficiency, enhance safety, reduce environmental impact, and optimize their resources.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how GIS is reshaping the mining industry, driving innovation, and contributing to more sustainable and efficient operations.
GIS in Mineral Exploration: Unlocking the Earth’s Potential
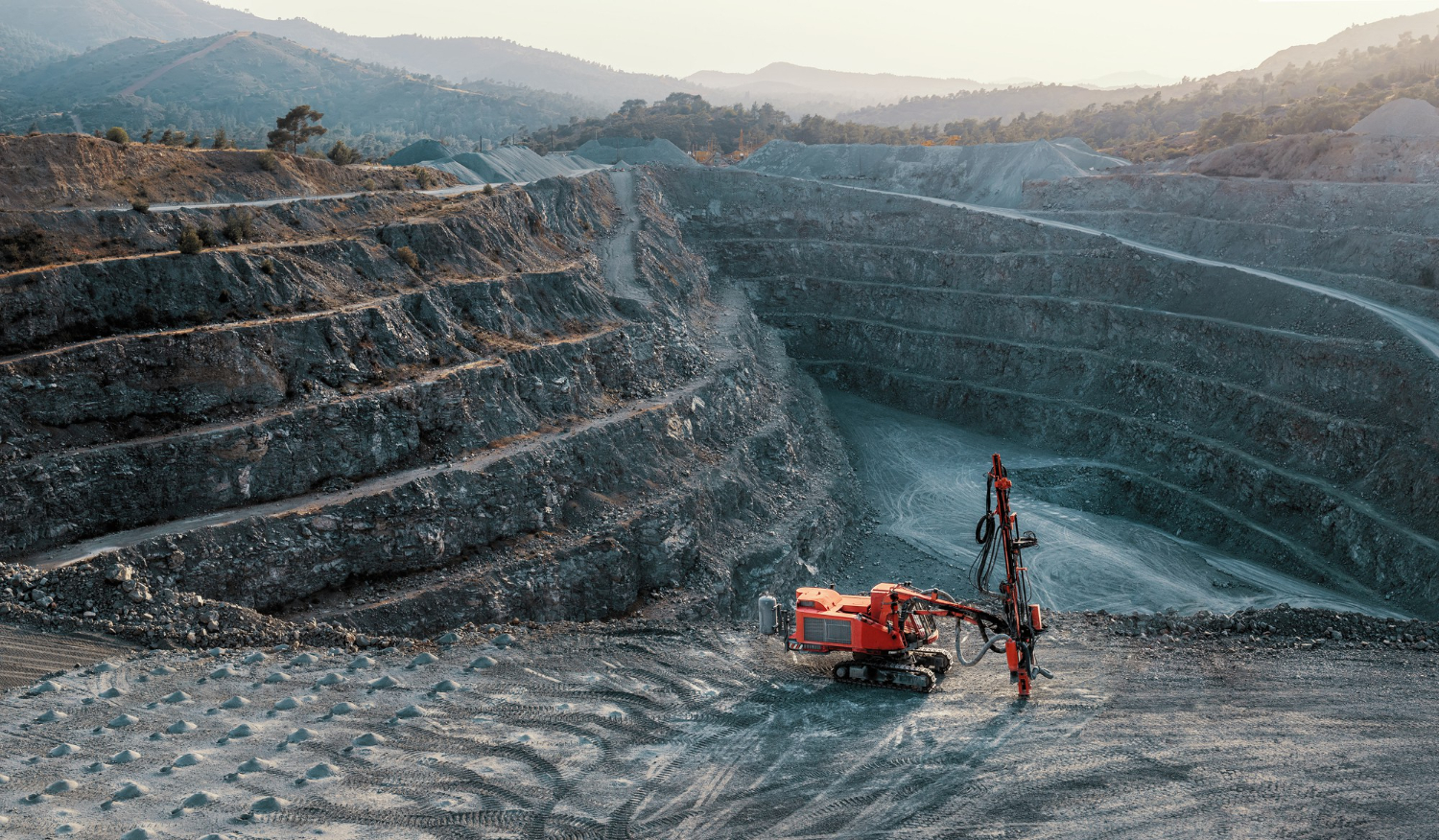
The process of mineral exploration involves identifying and evaluating new areas for mineral deposits. Traditionally, this could take years of field surveys and manual mapping, but with GIS, mining companies can analyze vast amounts of data in a fraction of the time.

GIS integrates geological data, satellite imagery, topographic maps, and other geospatial data into a single platform, enabling exploration teams to identify areas with the highest potential for discovery. For example, by overlaying geological maps with geophysical and geochemical survey data, GIS allows professionals to visualize subsurface features and pinpoint areas where valuable minerals are most likely to be found. This data-driven approach reduces the costs and risks associated with exploration while improving accuracy and success rates.
Site Planning and Development: Strategic Resource Allocation
Once mineral deposits are identified, GIS plays an essential role in site planning and mine development. GIS helps create detailed, accurate maps that represent both the surface and subsurface conditions of the mining site. These maps are essential for designing mining operations, as they provide a clear picture of the terrain, infrastructure, and natural resources.
For instance, GIS tools help in determining the optimal location for roads, infrastructure, waste disposal, and drilling operations. They also support 3D modeling to simulate different extraction methods and visualize how the mining operation will unfold over time. This helps mining companies plan for the most efficient use of resources and minimize disruptions to the local environment. 
Additionally, GIS allows companies to analyze the topography and landforms in the vicinity, which is essential for understanding potential environmental risks such as flooding, landslides, or erosion. This helps reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations and ensure long-term sustainability.
Optimizing Resource Management and Extraction
Efficiency is a critical component of successful mining operations, and GIS provides the tools to manage resources more effectively. Mining operations often involve multiple resources, including human labor, machinery, and raw materials, and it can be a challenge to coordinate and track these resources in real-time.
GIS integrates data from various sources such as GPS, sensors, and databases to monitor the status of mining activities. For example, GIS can track the movement of trucks carrying minerals, monitor equipment performance, and help mine operators predict maintenance needs. This real-time information enables companies to make data-driven decisions, ensuring smooth operations, reducing downtime, and maximizing productivity.

Furthermore, GIS enables precise mapping of ore bodies. By creating detailed 3D models of the mineral deposit, GIS helps operators optimize extraction methods, improving the efficiency of the mining process and reducing waste. This level of precision in planning can increase the profitability of mining operations while ensuring that the extraction process is as efficient and cost-effective as possible.
Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
Mining can have significant environmental impacts, which is why it is critical for companies to manage their operations in a way that minimizes harm to the environment. GIS plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing environmental factors during all stages of mining, from exploration to reclamation.
Before mining begins, GIS helps create baseline environmental data, such as mapping sensitive ecosystems, water sources, and protected areas. This data is critical for making informed decisions that avoid damaging environmentally sensitive regions.

During mining, GIS helps monitor water and air quality, track potential sources of contamination, and ensure that operations adhere to regulatory standards. For example, GIS tools can track the movement of wastewater or tailings, ensuring that they are properly managed and do not contaminate nearby rivers or groundwater.
After mining operations end, GIS is essential for monitoring reclamation efforts. By using remote sensing and geospatial data, mining companies can track the progress of land restoration and ensure that ecosystems are recovering. In this way, GIS supports more sustainable mining practices, promoting long-term environmental stewardship.
Safety and Risk Management: Ensuring Worker Well-being
Mining is a high-risk industry, and worker safety is always a top priority. GIS improves safety by providing real-time data on the location of workers, equipment, and potential hazards within the mine.
For instance, GIS allows companies to map out safe zones and evacuation routes, ensuring that workers know the safest paths in case of emergencies such as gas leaks or mine collapses. Additionally, GIS can integrate with wearable technologies (such as GPS tracking devices) to monitor the movement of personnel, ensuring that they are in designated safe areas and avoiding dangerous zones.

Moreover, GIS can model geotechnical conditions within the mine, such as rock stability, to predict potential hazards like cave-ins or rockfalls. By continuously monitoring conditions and using GIS for risk analysis, mining companies can take proactive measures to ensure worker safety and avoid costly accidents.
Logistics and Transportation: Streamlining Operations
Mining operations often require the transport of materials over long distances, sometimes through rugged or difficult terrain. GIS can help optimize transportation routes, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce costs.
By using GIS to analyze road conditions, traffic patterns, and weather data, mining companies can determine the most efficient routes for transporting ore, equipment, and supplies. This ensures that shipments are completed on time and at the lowest possible cost, while also helping to reduce the environmental impact of transportation.

In addition, GIS can help with the management of stockpiles and distribution of materials, ensuring that raw materials are moved efficiently from the mine to the processing plant or export terminal.
Post-Mining Reclamation and Closure
The closure of a mine is one of the most important stages of the mining lifecycle, and GIS plays an essential role in ensuring that mining operations are closed in an environmentally responsible manner. GIS is used to map and track the environmental condition of mining sites, plan for land reclamation, and monitor the success of these efforts over time.

Post-mining activities often involve remediating damaged ecosystems, restoring vegetation, and controlling erosion. GIS helps mining companies track and analyze these activities by creating accurate maps and spatial data on restored areas. Monitoring these areas over time ensures that the land is recovering and that the mine closure meets regulatory standards.
The Future of GIS in Mining
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the role of GIS in mining. The future will likely bring even more advanced technologies, such as drones, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, that will work in tandem with GIS to make mining operations more efficient, safe, and sustainable.

For example, drones equipped with sensors and cameras can gather high-resolution data from mining sites, which can then be processed and analyzed using GIS software. AI and machine learning can help predict mining outcomes, optimize resource extraction, and improve the accuracy of environmental monitoring.
GIS has become an indispensable tool for the mining industry, offering enhanced efficiency, better resource management, improved safety, and reduced environmental impact. By leveraging GIS, mining companies can streamline their operations from exploration to mine closure, ensuring they make informed decisions that drive profitability while preserving the environment.
As technology continues to advance, the role of GIS in mining will only grow more important. Whether it’s improving exploration accuracy, managing environmental risks, or ensuring worker safety, GIS is shaping the future of the mining industry, making it smarter, safer, and more sustainable.

- Vinaybabu Pasam
- December 26, 2024
How GIS Technology is Revolutionizing the Mining Industry
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) have rapidly evolved from a niche technology to a cornerstone of industries across the world, and the mining sector is no exception. GIS offers transformative solutions for nearly every phase of mining, from exploration to extraction, logistics, environmental management, and beyond. By combining spatial data with advanced analysis tools, GIS helps mining companies increase efficiency, enhance safety, reduce environmental impact, and optimize their resources.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how GIS is reshaping the mining industry, driving innovation, and contributing to more sustainable and efficient operations.
GIS in Mineral Exploration: Unlocking the Earth’s Potential
The process of mineral exploration involves identifying and evaluating new areas for mineral deposits. Traditionally, this could take years of field surveys and manual mapping, but with GIS, mining companies can analyze vast amounts of data in a fraction of the time.

GIS integrates geological data, satellite imagery, topographic maps, and other geospatial data into a single platform, enabling exploration teams to identify areas with the highest potential for discovery. For example, by overlaying geological maps with geophysical and geochemical survey data, GIS allows professionals to visualize subsurface features and pinpoint areas where valuable minerals are most likely to be found. This data-driven approach reduces the costs and risks associated with exploration while improving accuracy and success rates.
Site Planning and Development: Strategic Resource Allocation
Once mineral deposits are identified, GIS plays an essential role in site planning and mine development. GIS helps create detailed, accurate maps that represent both the surface and subsurface conditions of the mining site. These maps are essential for designing mining operations, as they provide a clear picture of the terrain, infrastructure, and natural resources.
For instance, GIS tools help in determining the optimal location for roads, infrastructure, waste disposal, and drilling operations. They also support 3D modeling to simulate different extraction methods and visualize how the mining operation will unfold over time. This helps mining companies plan for the most efficient use of resources and minimize disruptions to the local environment. 
Additionally, GIS allows companies to analyze the topography and landforms in the vicinity, which is essential for understanding potential environmental risks such as flooding, landslides, or erosion. This helps reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations and ensure long-term sustainability.
Optimizing Resource Management and Extraction
Efficiency is a critical component of successful mining operations, and GIS provides the tools to manage resources more effectively. Mining operations often involve multiple resources, including human labor, machinery, and raw materials, and it can be a challenge to coordinate and track these resources in real-time.
GIS integrates data from various sources such as GPS, sensors, and databases to monitor the status of mining activities. For example, GIS can track the movement of trucks carrying minerals, monitor equipment performance, and help mine operators predict maintenance needs. This real-time information enables companies to make data-driven decisions, ensuring smooth operations, reducing downtime, and maximizing productivity.

Furthermore, GIS enables precise mapping of ore bodies. By creating detailed 3D models of the mineral deposit, GIS helps operators optimize extraction methods, improving the efficiency of the mining process and reducing waste. This level of precision in planning can increase the profitability of mining operations while ensuring that the extraction process is as efficient and cost-effective as possible.
Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
Mining can have significant environmental impacts, which is why it is critical for companies to manage their operations in a way that minimizes harm to the environment. GIS plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing environmental factors during all stages of mining, from exploration to reclamation.
Before mining begins, GIS helps create baseline environmental data, such as mapping sensitive ecosystems, water sources, and protected areas. This data is critical for making informed decisions that avoid damaging environmentally sensitive regions.

During mining, GIS helps monitor water and air quality, track potential sources of contamination, and ensure that operations adhere to regulatory standards. For example, GIS tools can track the movement of wastewater or tailings, ensuring that they are properly managed and do not contaminate nearby rivers or groundwater.
After mining operations end, GIS is essential for monitoring reclamation efforts. By using remote sensing and geospatial data, mining companies can track the progress of land restoration and ensure that ecosystems are recovering. In this way, GIS supports more sustainable mining practices, promoting long-term environmental stewardship.
Safety and Risk Management: Ensuring Worker Well-being
Mining is a high-risk industry, and worker safety is always a top priority. GIS improves safety by providing real-time data on the location of workers, equipment, and potential hazards within the mine.
For instance, GIS allows companies to map out safe zones and evacuation routes, ensuring that workers know the safest paths in case of emergencies such as gas leaks or mine collapses. Additionally, GIS can integrate with wearable technologies (such as GPS tracking devices) to monitor the movement of personnel, ensuring that they are in designated safe areas and avoiding dangerous zones.

Moreover, GIS can model geotechnical conditions within the mine, such as rock stability, to predict potential hazards like cave-ins or rockfalls. By continuously monitoring conditions and using GIS for risk analysis, mining companies can take proactive measures to ensure worker safety and avoid costly accidents.
Logistics and Transportation: Streamlining Operations
Mining operations often require the transport of materials over long distances, sometimes through rugged or difficult terrain. GIS can help optimize transportation routes, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce costs.
By using GIS to analyze road conditions, traffic patterns, and weather data, mining companies can determine the most efficient routes for transporting ore, equipment, and supplies. This ensures that shipments are completed on time and at the lowest possible cost, while also helping to reduce the environmental impact of transportation.

In addition, GIS can help with the management of stockpiles and distribution of materials, ensuring that raw materials are moved efficiently from the mine to the processing plant or export terminal.
Post-Mining Reclamation and Closure
The closure of a mine is one of the most important stages of the mining lifecycle, and GIS plays an essential role in ensuring that mining operations are closed in an environmentally responsible manner. GIS is used to map and track the environmental condition of mining sites, plan for land reclamation, and monitor the success of these efforts over time.

Post-mining activities often involve remediating damaged ecosystems, restoring vegetation, and controlling erosion. GIS helps mining companies track and analyze these activities by creating accurate maps and spatial data on restored areas. Monitoring these areas over time ensures that the land is recovering and that the mine closure meets regulatory standards.
The Future of GIS in Mining
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the role of GIS in mining. The future will likely bring even more advanced technologies, such as drones, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, that will work in tandem with GIS to make mining operations more efficient, safe, and sustainable.

For example, drones equipped with sensors and cameras can gather high-resolution data from mining sites, which can then be processed and analyzed using GIS software. AI and machine learning can help predict mining outcomes, optimize resource extraction, and improve the accuracy of environmental monitoring.
GIS has become an indispensable tool for the mining industry, offering enhanced efficiency, better resource management, improved safety, and reduced environmental impact. By leveraging GIS, mining companies can streamline their operations from exploration to mine closure, ensuring they make informed decisions that drive profitability while preserving the environment.
As technology continues to advance, the role of GIS in mining will only grow more important. Whether it’s improving exploration accuracy, managing environmental risks, or ensuring worker safety, GIS is shaping the future of the mining industry, making it smarter, safer, and more sustainable.