Evolution of Geospatial technology and emerging trends in the industry

- Yogesh Karyakarte
- October 20, 2022
A few years back, if you had to travel from point A to point B and had never been to that area, you had to depend on the local people for directions. A few would know the exact direction. Depending on how busy they were, they directed you to your required destination. Sometimes they may also misguide you. You might have also traveled to a remote area where no one is around to help get the direction. What would you have done in such a scenario? Fortunately, remote sensing and GIS have come up with innovative techniques and methodologies that have enabled us not only to pinpoint your location but also to find the best route to your required location. This is just one example of the use of GIS technology. GIS now helps us to manage our day-to-day activities, and we are totally dependent on it. Did this happen overnight? No. Like other technologies, GIS also had its evolution. Academic institutes and governments first started using computer aided system to create and analyze geographical datasets. Progressively people got involved in data creation, analysis, and software development. Numerous geographers, planners, computer scientists, and others from many fields came together to create the first visualization and spatial analysis software. ESRI, one of the well-known companies, was established in 1969 to help land use planners and land resource managers to make informed decisions. GIS has come a long way since it was first used in the 1960s.
Today, GIS technology is used in various industries for decision making. ESRI is one of the largest and oldest companies which is providing end to end GIS solutions for industries viz Mining, Retail, Agriculture, Architecture, Engineering, and Construction, Asset Management, Financial Services, Insurance, Logistics and Distribution, Real Estate, Utilities, Aviation, Natural Resources, Forestry, Petroleum, Renewables, Telecommunications, Transportation etc.
 Though multiple open-source GIS software exists, ESRI provides users with the most advanced, user-friendly GIS platforms. Due to its simplicity, learning ArcGIS is very quick. In contrast, open-source software takes a lot of time to understand processes. ArcGIS allows you to understand your data more intuitively. Various important spatial datasets are made available through the living atlas and Indo-ArcGIS. These datasets are not readily available anywhere else. One can easily import these datasets into ArcGIS platforms for desired analysis.
Though multiple open-source GIS software exists, ESRI provides users with the most advanced, user-friendly GIS platforms. Due to its simplicity, learning ArcGIS is very quick. In contrast, open-source software takes a lot of time to understand processes. ArcGIS allows you to understand your data more intuitively. Various important spatial datasets are made available through the living atlas and Indo-ArcGIS. These datasets are not readily available anywhere else. One can easily import these datasets into ArcGIS platforms for desired analysis.ArcGIS also has various readily available robust tools that do not need separate installations (plugins). ArcGIS model builder allows building models to reduce the processing time for iterative processes. ArcGIS provides Arc Scene and Arc Globe for 3D visualization and data processing. One can easily import data from ArcMap to Arc Scene on the fly. It is easy to create and share maps through ArcGIS online. Even previously created maps in ArcMap can be published as web maps through ArcGIS online. Using these maps, one can also create story maps. We can narrate the story using text, maps, and multimedia, making it attractive and easily understood by the audience.
ArcGIS provides industry specific robust geoprocessing tools for fast and easy analysis. Using a business analyst tool, a retail company can easily find locations of their potential customers, check market penetration, and focus on expansion in that area. Using image processing tools such as change detection, one can find the pixel level changes or the Matic changes in Land Use Land Cover in a few clicks. This tool provides statistics such as the conversion from one class to another or several other specified classes. These tools are very user friendly and intuitive, so a new user can use them without much guidance.
Meanwhile, ESRI provides self-paced web-based training for beginners and experts. ESRI offers in-depth documentation on how to use tools and delivers sample data for you to get hands-on experience. The training and software updates for open-source software are often not structured well.
ESRI provides end-to-end solutions. For example, it provides platforms for data collection, manipulation, and presentations. These apps/tools are interlinked and updated in live. Hence, as soon as data is updated by field staff using Field collector or Survey123, it gets updated on online maps. The data can also be published in dashboards, story maps, and even ArcGIS hub (where you can create your websites).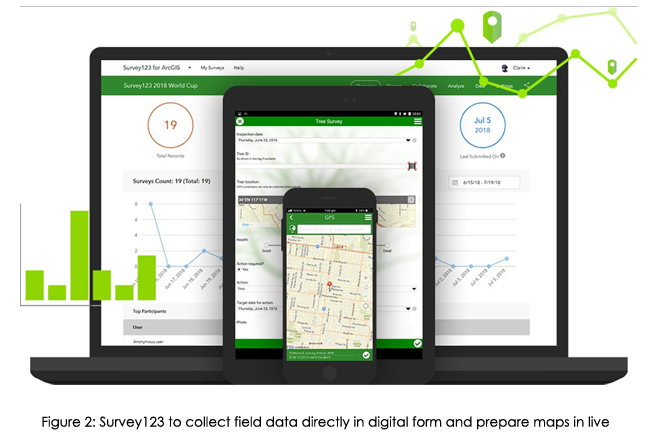
As soon as you install a particular solution, all the relevant tools and apps get installed in your system, which you can customize and deploy for your stakeholders. ESRI also provide APIs and SDKs for customization so organizations can develop the ESRI software/apps as per their own need.
A few of the app needs installation on a laptop/desktop. While ESRI cloud platforms such as ArcGIS online, Site Scan, ArcGIS velocity, etc. do not require installation, users can sign in and use these platforms from any computer system. ArcGIS Online is a Cloud-based software to create and share interactive web maps. Site Scan for ArcGIS is the end-to-end cloud-based drone mapping software designed to revolutionize imagery data collection, processing, and analysis. ArcGIS velocity enables users to ingest data from the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, message brokers, or third-party APIs. It also helps users process, visualize, and analyze real-time data feeds; store these as big data, and perform fast queries and analyses.
ArcGIS Business Analyst
It is a extension that helps you make smarter decisions for market planning, site selection, and customer segmentation by combining demographic, business, lifestyle, spending, and census data with map-based analytics. Business Analyst helps you identify underperforming markets, pinpoint the suitable growth sites, find where your target customers live, and share the analysis across your organization as accurate infographic reports and dynamic presentations.
ArcGIS CityEngine
It is a stand-alone software product that provides a design and modeling solution for efficiently creating 3D cities.
To know more about upcoming GIS technologies and to understand how to use ESRI platforms for your business, please get in touch with us at edst@edstechnologies.com

- Yogesh Karyakarte
- October 20, 2022
Evolution of Geospatial technology and emerging trends in the industry
A few years back, if you had to travel from point A to point B and had never been to that area, you had to depend on the local people for directions. A few would know the exact direction. Depending on how busy they were, they directed you to your required destination. Sometimes they may also misguide you. You might have also traveled to a remote area where no one is around to help get the direction. What would you have done in such a scenario? Fortunately, remote sensing and GIS have come up with innovative techniques and methodologies that have enabled us not only to pinpoint your location but also to find the best route to your required location. This is just one example of the use of GIS technology. GIS now helps us to manage our day-to-day activities, and we are totally dependent on it. Did this happen overnight? No. Like other technologies, GIS also had its evolution. Academic institutes and governments first started using computer aided system to create and analyze geographical datasets. Progressively people got involved in data creation, analysis, and software development. Numerous geographers, planners, computer scientists, and others from many fields came together to create the first visualization and spatial analysis software. ESRI, one of the well-known companies, was established in 1969 to help land use planners and land resource managers to make informed decisions. GIS has come a long way since it was first used in the 1960s.
Today, GIS technology is used in various industries for decision making. ESRI is one of the largest and oldest companies which is providing end to end GIS solutions for industries viz Mining, Retail, Agriculture, Architecture, Engineering, and Construction, Asset Management, Financial Services, Insurance, Logistics and Distribution, Real Estate, Utilities, Aviation, Natural Resources, Forestry, Petroleum, Renewables, Telecommunications, Transportation etc.
 Though multiple open-source GIS software exists, ESRI provides users with the most advanced, user-friendly GIS platforms. Due to its simplicity, learning ArcGIS is very quick. In contrast, open-source software takes a lot of time to understand processes. ArcGIS allows you to understand your data more intuitively. Various important spatial datasets are made available through the living atlas and Indo-ArcGIS. These datasets are not readily available anywhere else. One can easily import these datasets into ArcGIS platforms for desired analysis.
Though multiple open-source GIS software exists, ESRI provides users with the most advanced, user-friendly GIS platforms. Due to its simplicity, learning ArcGIS is very quick. In contrast, open-source software takes a lot of time to understand processes. ArcGIS allows you to understand your data more intuitively. Various important spatial datasets are made available through the living atlas and Indo-ArcGIS. These datasets are not readily available anywhere else. One can easily import these datasets into ArcGIS platforms for desired analysis.ArcGIS also has various readily available robust tools that do not need separate installations (plugins). ArcGIS model builder allows building models to reduce the processing time for iterative processes. ArcGIS provides Arc Scene and Arc Globe for 3D visualization and data processing. One can easily import data from ArcMap to Arc Scene on the fly. It is easy to create and share maps through ArcGIS online. Even previously created maps in ArcMap can be published as web maps through ArcGIS online. Using these maps, one can also create story maps. We can narrate the story using text, maps, and multimedia, making it attractive and easily understood by the audience.
ArcGIS provides industry specific robust geoprocessing tools for fast and easy analysis. Using a business analyst tool, a retail company can easily find locations of their potential customers, check market penetration, and focus on expansion in that area. Using image processing tools such as change detection, one can find the pixel level changes or the Matic changes in Land Use Land Cover in a few clicks. This tool provides statistics such as the conversion from one class to another or several other specified classes. These tools are very user friendly and intuitive, so a new user can use them without much guidance.
Meanwhile, ESRI provides self-paced web-based training for beginners and experts. ESRI offers in-depth documentation on how to use tools and delivers sample data for you to get hands-on experience. The training and software updates for open-source software are often not structured well.
ESRI provides end-to-end solutions. For example, it provides platforms for data collection, manipulation, and presentations. These apps/tools are interlinked and updated in live. Hence, as soon as data is updated by field staff using Field collector or Survey123, it gets updated on online maps. The data can also be published in dashboards, story maps, and even ArcGIS hub (where you can create your websites).
As soon as you install a particular solution, all the relevant tools and apps get installed in your system, which you can customize and deploy for your stakeholders. ESRI also provide APIs and SDKs for customization so organizations can develop the ESRI software/apps as per their own need.
A few of the app needs installation on a laptop/desktop. While ESRI cloud platforms such as ArcGIS online, Site Scan, ArcGIS velocity, etc. do not require installation, users can sign in and use these platforms from any computer system. ArcGIS Online is a Cloud-based software to create and share interactive web maps. Site Scan for ArcGIS is the end-to-end cloud-based drone mapping software designed to revolutionize imagery data collection, processing, and analysis. ArcGIS velocity enables users to ingest data from the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, message brokers, or third-party APIs. It also helps users process, visualize, and analyze real-time data feeds; store these as big data, and perform fast queries and analyses.
ArcGIS Business Analyst
It is a extension that helps you make smarter decisions for market planning, site selection, and customer segmentation by combining demographic, business, lifestyle, spending, and census data with map-based analytics. Business Analyst helps you identify underperforming markets, pinpoint the suitable growth sites, find where your target customers live, and share the analysis across your organization as accurate infographic reports and dynamic presentations.
ArcGIS CityEngine
It is a stand-alone software product that provides a design and modeling solution for efficiently creating 3D cities.
To know more about upcoming GIS technologies and to understand how to use ESRI platforms for your business, please get in touch with us at edst@edstechnologies.com