Revolutionizing the Agriculture Sector with Data Driven GIS Solutions

- Aniket Rehpade
- December 25, 2024
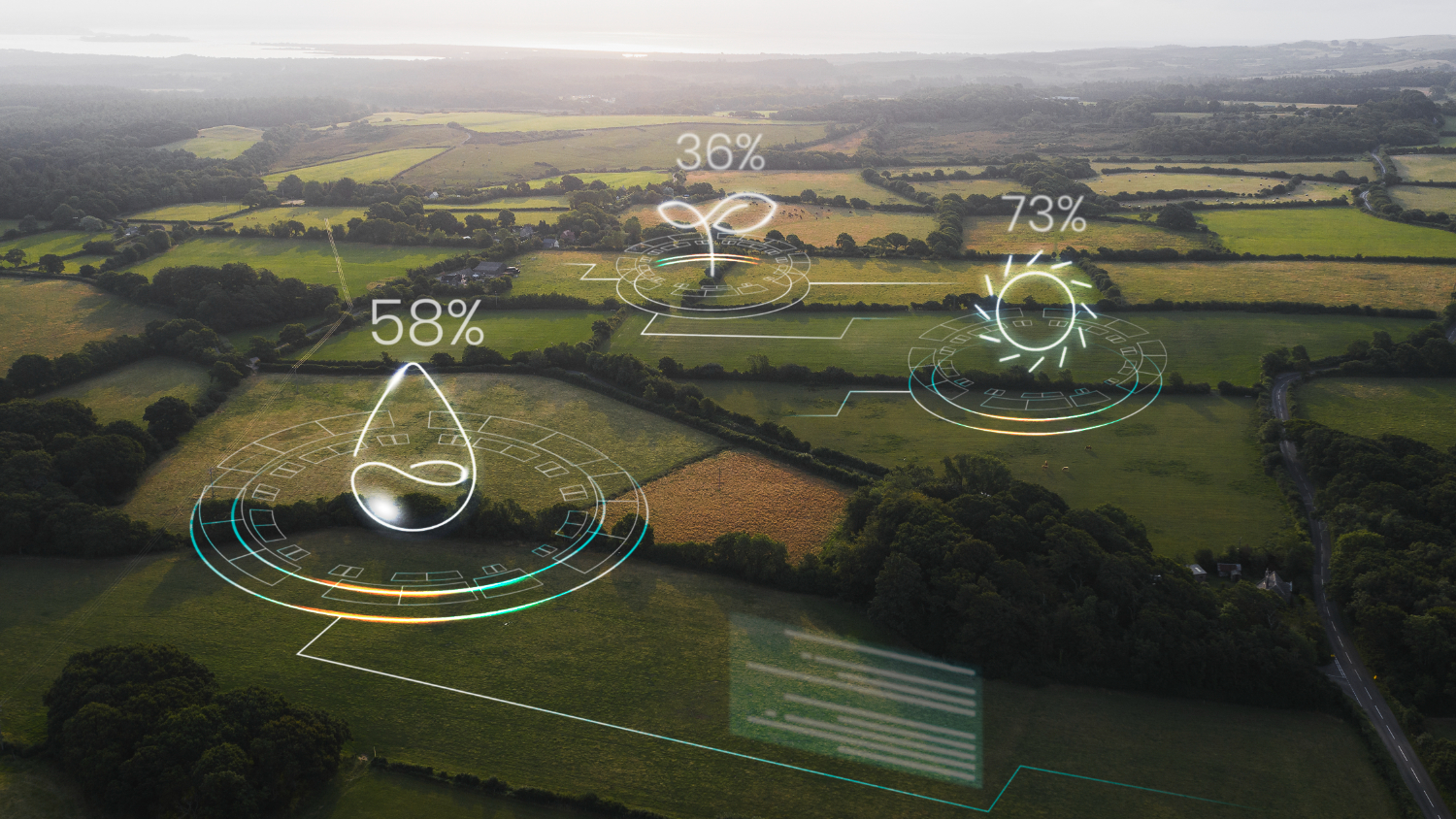
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is emerging technology in India which is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.45 per cent. The application has solutions right from transport and mobility, retail, infrastructure, agriculture to homeland security. The agriculture sector has seen a massive growth with the GIS solution to improve the efficiency and productivity of farming operations right from crop cultivation decisoin, monitoring, irrigation market analysis, logistic to insurance.
GIS technology plays a crucial role in modern agriculture by providing spatial data and analytical tools that help farmers make informed decisions, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
Here are some key applications:
- Soil Analysis
- Precision Farming
- Crop Monitoring
- Irrigation Management
- Yield Prediction
- Farm Planning and Management
- Crop Insurance
Soil Analysis
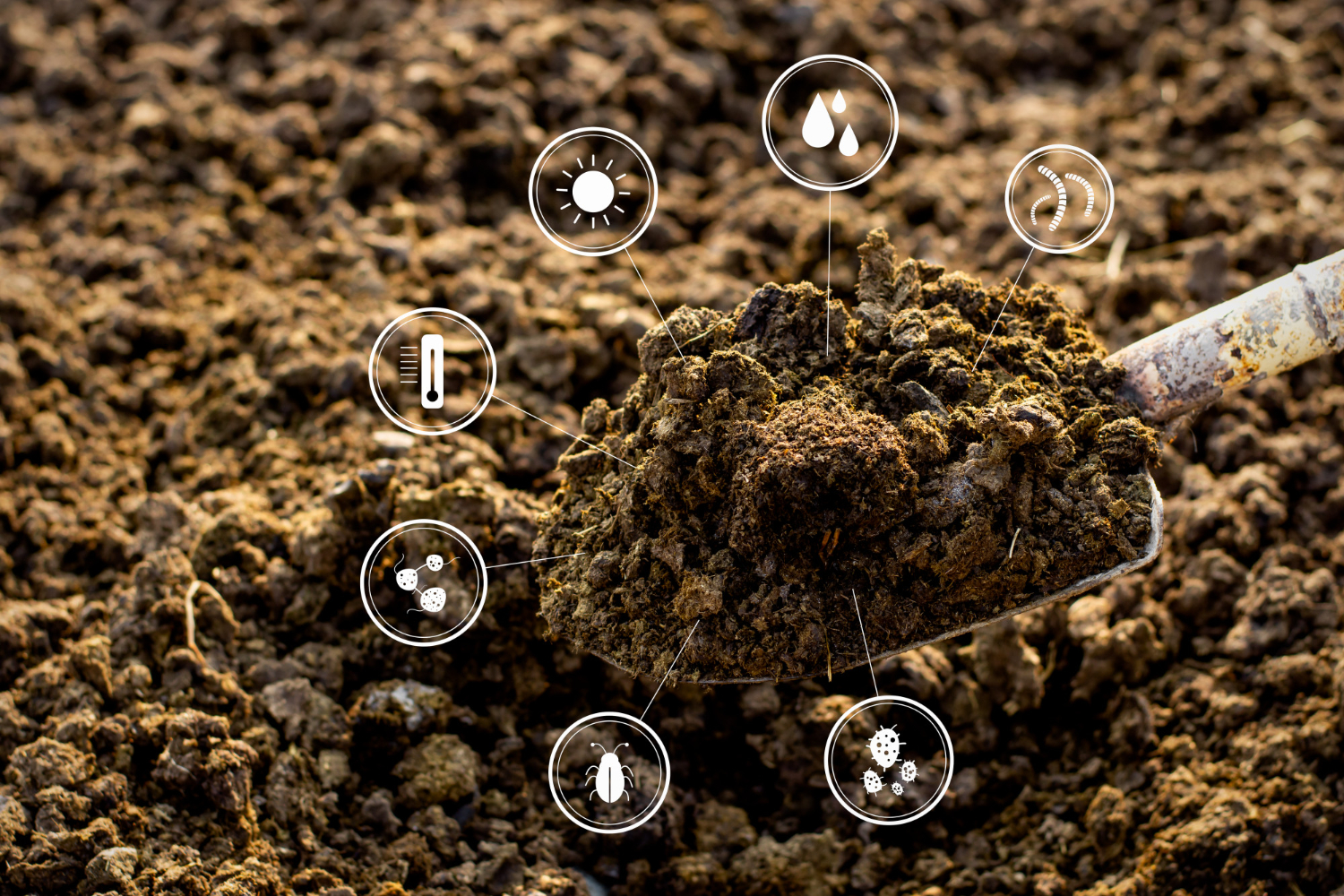

By spatially mapping soil types and their inherent properties, GIS facilitates a comprehensive understanding of soil health and fertility. This spatial analysis enables informed decisions regarding optimal crop selection and the precise application of soil amendments, ultimately enhancing agricultural productivity and resource efficiency.
Precision Farming

Integrating spatial data on soil characteristics, crop health, and environmental conditions, GIS empowers farmers to implement precision farming practices. This data-driven approach enables optimized resource management through site-specific application of inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides. Consequently, farmers can minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and enhance crop yields by tailoring agricultural practices to the unique requirements of each field area.
Crop Monitoring
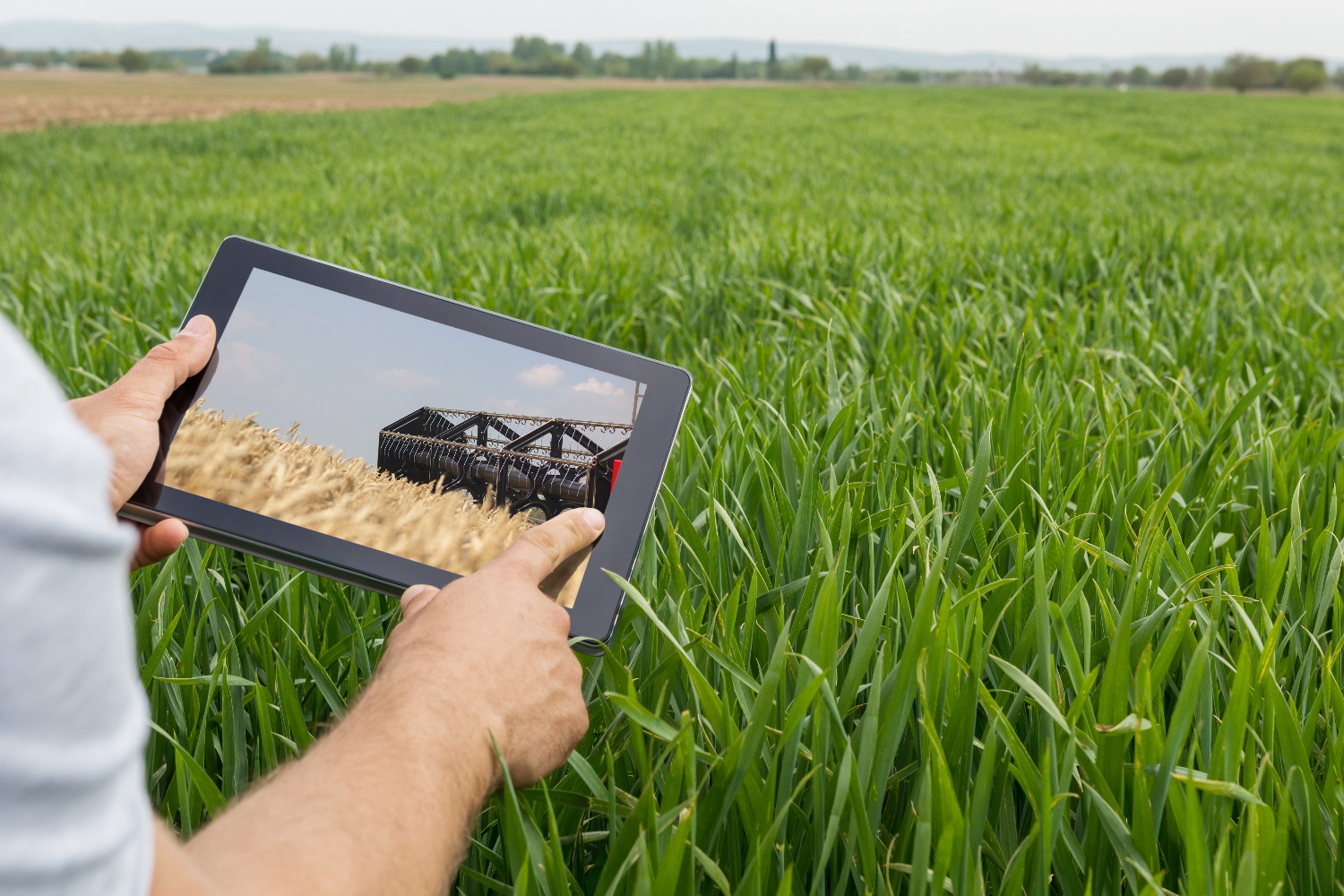

By enabling continuous monitoring of crop conditions and growth patterns. Leveraging satellite imagery and remote sensing data, farmers gain valuable insights into crop health. This allows for early detection of potential issues, such as disease outbreaks or pest infestations, facilitating timely interventions and optimizing crop management strategies.
Irrigation Management
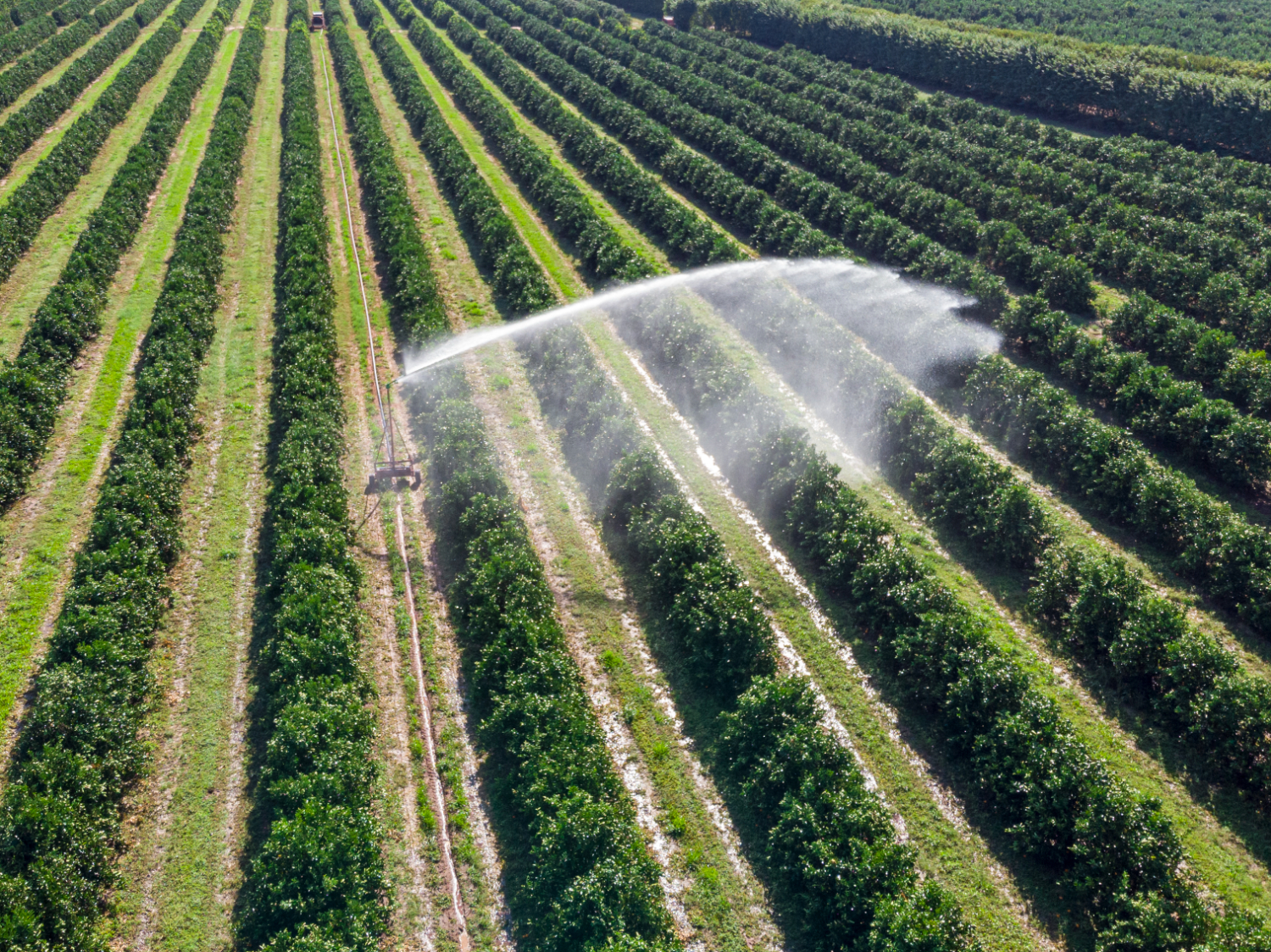

The design of efficient irrigation systems by enabling the mapping of water resources and soil moisture levels. This spatial analysis allows for precise irrigation scheduling, ensuring crops receive the optimal amount of water at the appropriate time. Consequently, water resources are conserved, and crop health is significantly improved.
Yield Prediction
By analyzing historical yield data in conjunction with current crop conditions, GIS facilitates accurate crop yield prediction. This valuable information empowers stakeholders in the agricultural sector, including farmers, processors, and distributors, to effectively plan and manage supply chains, ensuring efficient resource allocation and mitigating potential market disruptions.
Farm Planning and Management

GIS provides critical support for the planning and management of farm operations. By facilitating the spatial analysis of farm layouts, crop rotation schedules, and the distribution of farm infrastructure, GIS enables optimized land use and streamlined farm management practices. This integrated approach contributes to increased efficiency and improved overall farm productivity.
Crop Insurance

GIS technology allows insurers to accurately map and analyze agricultural areas, identify potential hazards, and monitor crop health. By integrating satellite imagery, weather data, and historical crop performance, GIS provides comprehensive insights that help insurers make informed decisions, set fair premiums, and expedite claims processing. This advanced approach not only mitigates financial risks for farmers but also ensures timely support, fostering a more resilient agricultural sector.
Market Analysis

GIS empowers businesses to conduct sophisticated market analyses by providing valuable insights into market trends and optimizing transportation logistics. By integrating spatial data on consumer demographics, competitor locations, and market demand, GIS facilitates the identification of optimal locations for sales outlets and distribution centers, ultimately enhancing market penetration and profitability.
Conclusion
By leveraging GIS technology, farmers can optimize resource use, enhance crop management, and make data-driven decisions that lead to higher yields and sustainable practices. From soil analysis and irrigation management to crop monitoring and disaster preparedness, the applications of GIS are vast and impactful. As the agricultural sector continues to face challenges such as climate change and the need for increased food production, GIS provides a powerful tool to meet these demands.
Reach out to us to deep dive into the technical capabilities and understand how GIS is transforming the agriculture sector with data-driven information.

- Aniket Rehpade
- December 25, 2024
Revolutionizing the Agriculture Sector with Data Driven GIS Solutions
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is emerging technology in India which is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.45 per cent. The application has solutions right from transport and mobility, retail, infrastructure, agriculture to homeland security. The agriculture sector has seen a massive growth with the GIS solution to improve the efficiency and productivity of farming operations right from crop cultivation decisoin, monitoring, irrigation market analysis, logistic to insurance.
GIS technology plays a crucial role in modern agriculture by providing spatial data and analytical tools that help farmers make informed decisions, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
Here are some key applications:
- Soil Analysis
- Precision Farming
- Crop Monitoring
- Irrigation Management
- Yield Prediction
- Farm Planning and Management
- Crop Insurance
Soil Analysis

By spatially mapping soil types and their inherent properties, GIS facilitates a comprehensive understanding of soil health and fertility. This spatial analysis enables informed decisions regarding optimal crop selection and the precise application of soil amendments, ultimately enhancing agricultural productivity and resource efficiency.
Precision Farming

Integrating spatial data on soil characteristics, crop health, and environmental conditions, GIS empowers farmers to implement precision farming practices. This data-driven approach enables optimized resource management through site-specific application of inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides. Consequently, farmers can minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and enhance crop yields by tailoring agricultural practices to the unique requirements of each field area.
Crop Monitoring

By enabling continuous monitoring of crop conditions and growth patterns. Leveraging satellite imagery and remote sensing data, farmers gain valuable insights into crop health. This allows for early detection of potential issues, such as disease outbreaks or pest infestations, facilitating timely interventions and optimizing crop management strategies.
Irrigation Management

The design of efficient irrigation systems by enabling the mapping of water resources and soil moisture levels. This spatial analysis allows for precise irrigation scheduling, ensuring crops receive the optimal amount of water at the appropriate time. Consequently, water resources are conserved, and crop health is significantly improved.
Yield Prediction

By analyzing historical yield data in conjunction with current crop conditions, GIS facilitates accurate crop yield prediction. This valuable information empowers stakeholders in the agricultural sector, including farmers, processors, and distributors, to effectively plan and manage supply chains, ensuring efficient resource allocation and mitigating potential market disruptions.
Farm Planning and Management

GIS provides critical support for the planning and management of farm operations. By facilitating the spatial analysis of farm layouts, crop rotation schedules, and the distribution of farm infrastructure, GIS enables optimized land use and streamlined farm management practices. This integrated approach contributes to increased efficiency and improved overall farm productivity.
Crop Insurance

GIS technology allows insurers to accurately map and analyze agricultural areas, identify potential hazards, and monitor crop health. By integrating satellite imagery, weather data, and historical crop performance, GIS provides comprehensive insights that help insurers make informed decisions, set fair premiums, and expedite claims processing. This advanced approach not only mitigates financial risks for farmers but also ensures timely support, fostering a more resilient agricultural sector.
Market Analysis

GIS empowers businesses to conduct sophisticated market analyses by providing valuable insights into market trends and optimizing transportation logistics. By integrating spatial data on consumer demographics, competitor locations, and market demand, GIS facilitates the identification of optimal locations for sales outlets and distribution centers, ultimately enhancing market penetration and profitability.
Conclusion
By leveraging GIS technology, farmers can optimize resource use, enhance crop management, and make data-driven decisions that lead to higher yields and sustainable practices. From soil analysis and irrigation management to crop monitoring and disaster preparedness, the applications of GIS are vast and impactful. As the agricultural sector continues to face challenges such as climate change and the need for increased food production, GIS provides a powerful tool to meet these demands.
Reach out to us to deep dive into the technical capabilities and understand how GIS is transforming the agriculture sector with data-driven information.