
A Deep Dive into the Future of Additive Manufacturing
Part 1: What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive Manufacturing (AM):
Additive Manufacturing (AM), commonly referred to as 3D printing is a manufacturing process to form 3D physical parts from CAD DATA. In AM process, hundreds or thousands of layers come together to form the physical 3-dimensional part by means of either binders or direct energy deposited on the material.
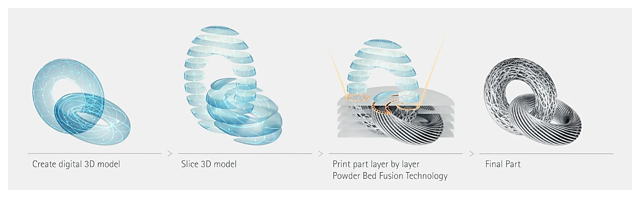
Due to very short lead time involved in the development of parts, the AM process used for manufacturing the prototypes rapidly is referred to as Rapid Prototyping. AM has gradually attained its importance in many industries like Aerospace, Healthcare etc. where use cases are proven for series or batch production also. This is only possible through high throughput and productivity of the latest systems that companies like EOS GmBH are manufacturing to yield the best of its productivity and optimized outcome. This brings down the ultimate cost of the parts produced through AM process.
Benefits of Industrial AM Process:
- Tool free technology to develop parts through only Digital Data.
- Short lead time to market.
- High performance materials engineered for different applications.
- High accuracy in first outcome.
- Design Flexibility at any time.
- High Repeatability with systems like EOS.
- Sustainability due to less environmental impact and sustainable material supply chain.
- Material reusability of highly efficient AM processes like SLS and DMLS.
- High strength of the printed materials in AM processes like SLS and DMLS.
- Reduced Physical inventory and practical possibility for JIT in supply chain.
Workflow of Industrial AM Process:
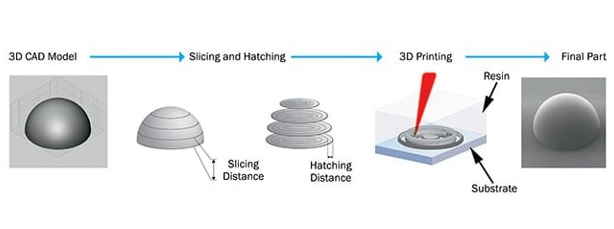
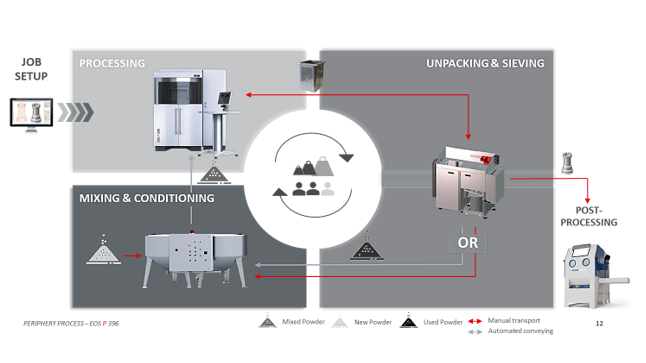
The Industrial AM process typically involves three stages –
- Pre-processing (Designing/ Data Preparation/ Build Simulation/ Build Optimization/ Slicing/ Programming for 3D printer or Parameter Assignment)
- Printing Process and
- Post Processing (Depowdering/ cleaning/ shot blasting/ Heat treatment/ support removal/ post machining etc.)
Classification of Industrial Additive Manufacturing:
Based on the raw material form, energy source used and technology workflow, the AM process is broadly classified into 7 Categories as follows:
- VAT Photopolymerization
- Material Jetting
- Binder Jetting
- Material Extrusion
- Powder Bed Fusion
- Sheet Lamination
- Direct Energy Deposition
We shall discuss in detail about the above categories and subcategories of the AM processes in coming series.

Arun K. Kashyap is a seasoned professional with an M. Tech. in Design Engineering. Currently serving as Manager – AM Technology at EDS Technologies Pvt. Ltd., he’s a Subject Matter Expert in Prototype Development using Laser Powder Bed Fusion. With over 8 years of experience, Arun is a trailblazer in design and product prototype development.
